- today(): Rainbird is able to generate today’s date at midnight as a value (e.g. if it’s the 2nd of February 2021, Rainbird would generate 2021-02-02 00:00:00) and use the value in expressions.
- now(): Rainbird is able to generate the date and time the query is run at as a value(e.g. if it’s the 2nd of February 2021 12PM, Rainbird would generate 2021-02-02 12:00:00) and use the value in expressions.
- 1000 (seconds)
- 60000 (minutes)
- 3600000 (hours)
- 86400000 (days)
- 31536000000 (years).
First, create two string concepts: ‘Person’ and ‘Greeting’. Next, connect the concepts with a relationship, ‘says’:

Figure 1: ‘Person’ and ‘Greeting’ concept linked with ‘says’ relationship
Next, create three concept instances for the concept ‘Greeting’:
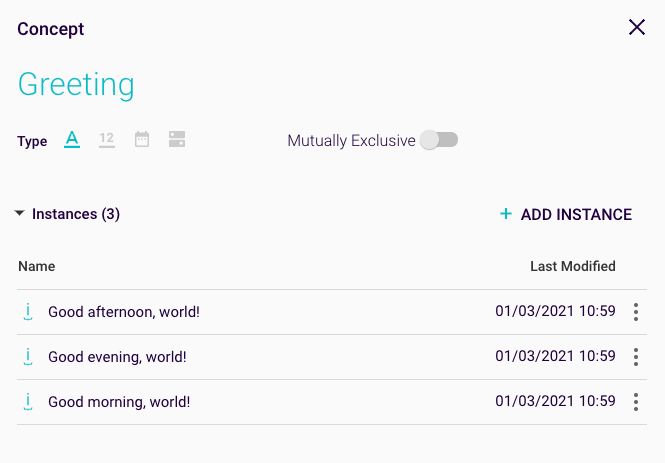
Figure 2: ‘Greeting’ concept instances
The three rules that the map will use are built on the relationship ‘says’.
Rainbird will work out what time of day it is, by comparing the value generated by the today() expression with the value generated by the now() expression.
Each rule needs a now() expression, as Rainbird will need to first work out what time it currently is. The expression is assigned to the variable %NOW:
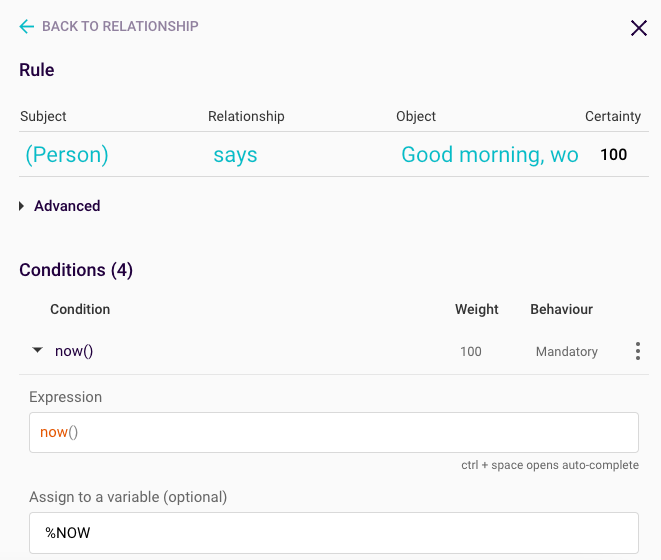
Figure 3: now() expression for ‘good morning’ rule
Each rule will also need a today() expression, as Rainbird will compare the now() value with the today() value, to see how many hours have passed in the day. As the value generated by the today() expression will be the time at midnight, the value will be assigned to the variable %MIDNIGHT:
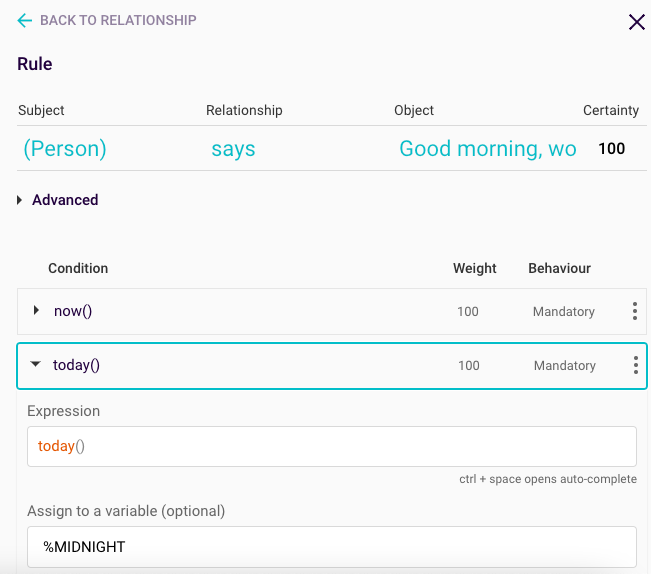
Figure 4: today() expression for ‘good morning’ rule
Now that we have created the expressions which will generate the values and assign the values to the variables %MIDNIGHT and %NOW, we need to use another expression to compare the two values. The Date Expressions ‘hoursBetween’ will count every full hour between the first hour of today’s date (%MIDNIGHT) and the time that the query is run (%NOW). The value calculated by the expression is assigned to the value %HOURS:
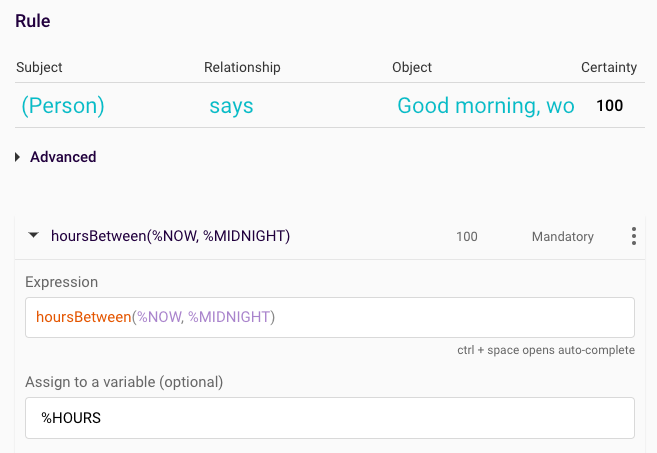
Figure 5: hoursbetween expression comparing the hours between %NOW and %MIDNIGHT
The %HOURS value will be the value compared with the hours of the day. We only want the map to return a ‘good morning’ result if the query is run before 12PM. So, the %HOURS value needs to be less than 12. Therefore, the final part of the rule would be:
Good morning:
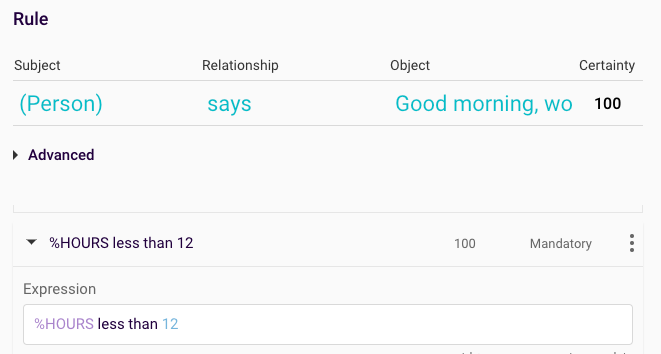
Figure 6: %HOURS less than 12 expression
To create the two rules for the ‘good afternoon’ and ‘good evening’ concept instances, follow the same steps above but change the final comparative expression, depending on the object of the rule.
Good afternoon:
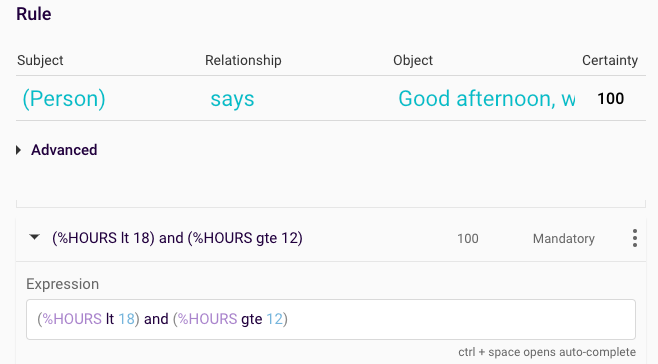
Figure 7: Good afternoon comparative expression
Good evening:
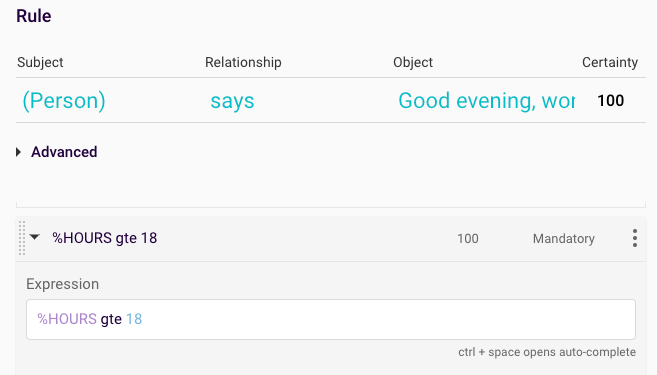
Figure 8: Good evening comparative expression
The ‘says’ query will return a different result, depending on when the query is run:
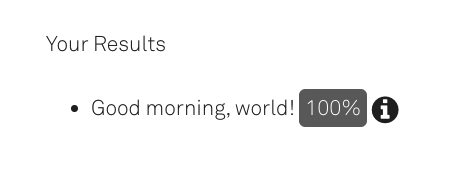
Figure 9: Result after running the main query ‘says’ before 12pm
Rainbird will output the values generated by the today() and now() expressions as the number of milliseconds passed since 1st of January 1970 to today’s date at midnight for today() or the current date and time for now().
If you create a relationship between the person concept and the greeting concept used in the example map, and add the today() value as the sole expression in the relationship’s rule, and assign the value to %O, when running the query, Rainbird will return the millisecond value:
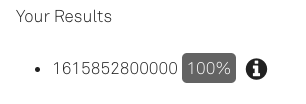
Figure 8: Millisecond value
The value can be converted into a more useful integer. To convert the value, create another relationship, ‘transformed in years’. To the rule on the ‘transformed in years’ relationship, add the following expressions:

Figure 9: Expressions to transform millisecond value to years and return the result as a string concatenation
You will need to assign the variable of the today() expression to %YEARS as Rainbird will use the %YEARS value in a string concatenation (the second expression), which will be the output of the query. The string concatenation will be assigned to the %O variable (the object of the relationship), as this is what we want Rainbird to return as a result.
Now, if you run the ‘transformed in years’ query, Rainbird will provide the following answer:

Figure 10: Transformed result
The RBLang below will generate the map that was built in the article. Click on ‘Export .rbird’ to download the knowledge map, or ‘copy RBLang’ and paste the code directly into Rainbird.
Query and Results
The query that will return a greeting depending on the time of day is on the ‘says’ relationship. The other two relationships, today and now, will display the date/current time in milliseconds.


